INDUSTRY NEWS
The Quiet Heroes: How Bearings Enable Progress

Bearings are mundane machine elements that enable society's most vital technologies to function. Though hidden within devices, bearings reduce friction for precision rotation on which performance, efficiency and reliability depend. Advancing fields from transportation and energy to healthcare and connectivity spur new demands for custom bearings to overcome extreme conditions. Meanwhile, achieving more sustainable, data-driven operations poses risks and opportunities across the global industry. Understanding bearing significance, diversity and trends provides insight into the forces driving continuous innovation.
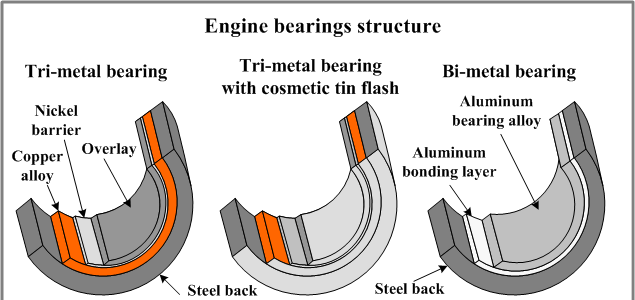
Types and Materials. The most common types are ball and roller bearings, using hardened steel balls/rollers between races. Plain, jewel and fluid bearings utilize non-rolling contacts for specific needs like insulation or high-speeds. New materials include ceramics for heat resistance, plastics for chemical endurance and magnetic alloys for levitation. Cages, seals and shields also influence performance based on operating environment. Lubricants reduce friction and corrosion but must suit bearing material, speed, load and temperature.
Applications. Bearings are essential for generating and transmitting power in industrial equipment, vehicles, aircraft, and wind/hydro turbines; enabling connectivity through computing, communications and robotic devices; improving healthcare via scanning, diagnosis, monitoring and surgical equipment; constructing buildings/infrastructure such as elevators, escalators, dams, bridges and rotating architectural structures; and advancing productivity/automation in sectors ranging from logistics to manufacturing. High-growth segments include EVs, robotics, medtech and renewables.
Technology and Trends. “Smart bearings” with embedded sensors enable predictive maintenance and optimization. Specialized bearings target sectors like aerospace, renewables and EVs. Plastic and fluid bearings suit corrosive environments. Sustainability means longer-life, renewable-lubricated and recycled bearings. However, these require investment in R&D and production at a time of margin pressure, talent gaps and disruptive change. Digital services, customization and alliances present opportunities for differentiation and new revenue streams to overcome risks.
Industry and Dynamics. The top bearing producers are SKF, Schaeffler, NSK, NTN, JTEKT and Timken, representing over 60% of an $100+ billion market. While growth tracks GDP, developing regions and technical sectors show greater increases. Automotive, industrial and aerospace segments dominate demand. Achieving technical and software capabilities to meet specialized needs strains resources and profits. Cost efficiency and sustainability drive manufacturing to Asia although technology centers remain in US, Europe and Japan.
Bearings empower monumental advances and underpin industries on which society depends, yet operate behind the scenes. Continuous innovation in precision, materials and efficiency overcomes barriers in sectors enabling a greener, more connected and productive future. By leveraging alliances and digital capabilities beyond components alone, companies can gain competitive advantage to navigate margin pressure, skills gaps and disruptive change. The future turns on the small but mighty bearing. Progress follows the path of least resistance.